Power consumption
To make it easy to find products that draw a little energy, there is a labeling system that applies to, among other things, TV sets. As modern products with LED technology consume less energy, the A rating has been supplemented with A +.

Here are the tips that the Swedish Competition Authority shares when authorities or other public enterprises are to buy TV.
Fairly large TV: There is a direct connection between the screen size and the energy consumption when the TV is on
Built-in digital box: A separate digital box can have an annual energy consumption that is as large as for a smaller TV.
At Avrop, requirements may be placed on environmental characteristics and social aspects, e.g. that distance-bridging technology should be used in order to reduce the number of trips, degree of energy efficiency, constituent materials, lack of conflict minerals and chemicals.
Light sensor: Mutes the TV picture when it gets darker in the room, which can reduce energy use by as much as 50 percent. It is best if the light sensor is adjustable.
Motion Sensor: Detects if someone is sitting in front of the TV and turns it off if the room is empty.
Hard shut-off button: Power button that turns off the TV completely.
For projectors, there are energy requirements at basic and advanced level that are based on TCO Development's requirements for projectors, which in addition to energy performance also take into account image quality. That the projector should have an echo mode and that it should automatically turn off when the interface to the projector is disconnected also provides a more energy efficient product.
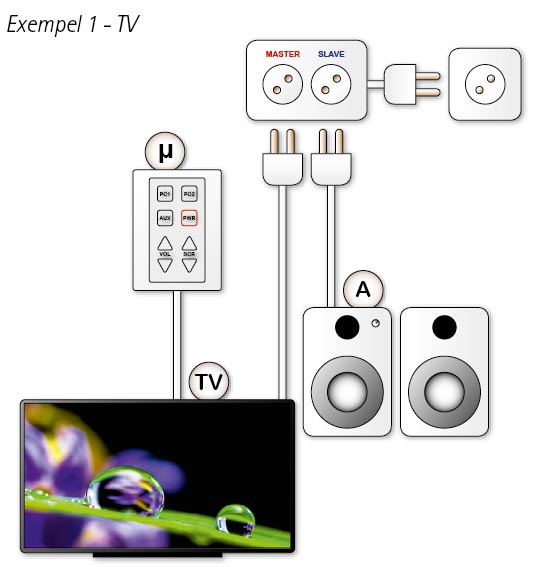
Smart energy-saving micro-control systems
Microcontroller systems are optimized to control AV systems and can save more energy than other solutions.
In example 1 above, a TV is connected to an energy-saving branch socket. The TV is controlled by the microsystem and the active speakers are switched off at the same time as the TV.
Advantages of this solution are, among other things, that the active speakers do not have to wait a time without sound to go into standby mode. There is also no risk that they go into stand-by mode in silent parts of a movie, for example. (What makes most users of "regular" auto-off speakers almost always opt out of the feature.)
In addition, you can continue to use your existing active speakers. Of course, throwing away a pair of working speakers and buying new ones with auto-off for environmental reasons counteracts its own purpose.
The more equipment that is connected - the more energy you can save.
In Example 2, a microsystem controls a data video projector.
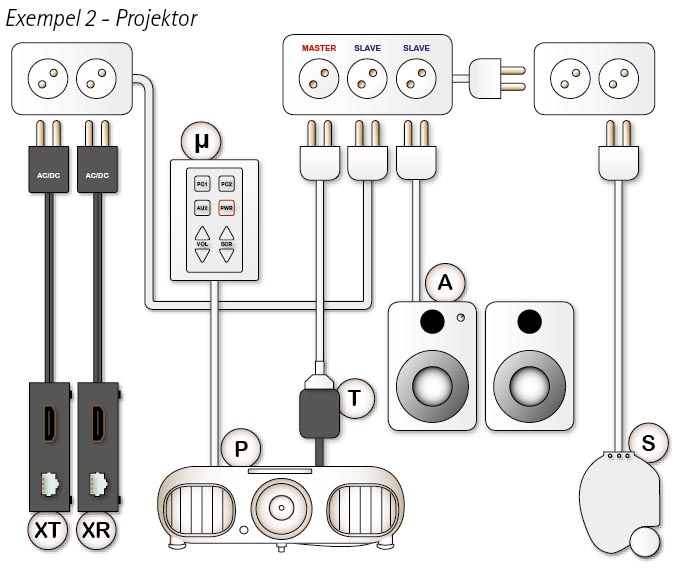
There is a trigger on the projector connection cable that detects when the projector is on. It sends a radio signal to the screen, which is rolled up or down depending on whether the projector is turned on or off. It can also roll down blinds in the room window. This means that you can have the projector in eco-mode, which gives a little weaker light but also quieter fan noise and longer operating time on the projector lamp.
To save battery life, manufacturers have made sure that the signals from a laptop are quite weak. The power is precisely adjusted to suffice for a screen in the immediate vicinity of the computer. In order for the signal to reach a projector that is mounted on the ceiling or on the wall, amplifiers are needed - so-called "extenders". In a regular meeting room, quite a few extenders for cameras and other things may be needed.
All of these draw power and they do so even after you turn off the office and go home. We avoid this by connecting them to the energy-saving junction box. The really valuable thing is that the whole facility still works exactly according to the user's needs.
It is still just as easy to control the meeting room and it consumes less energy overall than the strictest product requirements on the market.

Energy consumption at video meetings
When it comes to other equipment, it is the case that a desktop computer, for example, draws more power than a laptop. This is of course due to the fact that those who buy a battery-powered computer require a long operating time per charge, which means that the manufacturer chooses energy-efficient technology.
In a desktop computer, a low price or high performance applies and then it is only for the manufacturer to plug in a sufficiently powerful power supply.
Video conferencing and web conferencing
A webcam is an elegant solution because it is powered by the power from the computer's USB port. This means that it must consume relatively little energy to follow the USB specifications and for the computer's battery not to run out.
In addition, it is so certain that it is guaranteed not to draw any current at all when you unplug it from the computer.



So-called Codecar (signal conversion devices) for video conferencing can consume a surprising amount of energy. There is a link between the number of functions in a codec and its energy consumption, but it is more of a general rule.

Internet infrastructure
Another large energy consumer is quite rarely mentioned and for obvious reasons.
This applies to the infrastructure that ensures that all data arrives from your remote meeting solution to the recipient.
As you know, all data packets go over the internet at a breathtaking speed. This worldwide network of fiber, satellites, radio transmitters, cable, switches, hubs and giant data halls with many, many millions of servers. Greenpeace has calculated that if the internet were a country, it would be in sixth place in terms of energy consumption. In 2012, this corresponded to approximately 2% of carbon dioxide emissions, which is the same figure that applies to the world's commercial air traffic. In 2016, it had increased to 7%. From today to 2021, internet traffic is estimated to have tripled.
Green energy
A significant difference, however, is that the large data cloud can largely be driven by green energy, which the aviation industry has more difficulty with. Google, Facebook and even Apple (which struggled for a long time) now have large parts of their infrastructure powered by renewable energy sources.


However, some are still mainly powered by fossil fuels, such as Twitter and the American internet giant Amazon.
The type of energy used by all operators all the way to the one you have a distance meeting with is difficult to find out if it is not just around the corner. It is in the technology itself that the information can take slightly different paths. You can of course dig where you stand and talk to your own operator and hear what kind of energy they use.
You can also choose to use a fixed connection via fiber. It takes a little energy.
A mobile connection via the 3G network consumes a lot of energy (19.1kW per GB). This of course does not refer to the energy consumption in the phone itself but in transmitter masts and other things.

Summary
To make a long story short, it is currently best from an energy point of view to conduct video meetings:
By having a web meeting
with laptops
with built-in camera or USB camera
with fixed connection via optical fiber